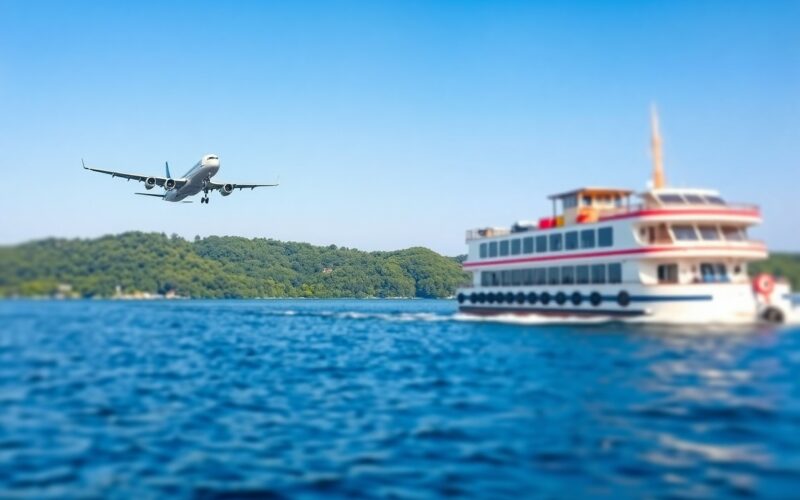
Over time, the impact of your travel choices on the environment has gained significant attention. Understanding the varying levels of CO2 emissions from different modes of transport is important for making more sustainable decisions. In this post, you will explore the environmental implications of flying, taking a train, or hopping on a ferry, helping you grasp the potential consequences of your travel habits. Delve into the facts and figures and learn more about Motorised transport: train, plane, road or boat — which is … to enhance your awareness of choosing greener travel options.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways:
- Traveling by train typically produces the lowest CO2 emissions per passenger compared to planes and ferries.
- Plane travel is generally the most carbon-intensive option, especially for short distances where the takeoff and landing phases significantly contribute to emissions.
- Ferries can vary widely in emissions based on the vessel type and size, but they often fall in between trains and planes in terms of environmental impact.
- Choosing more efficient modes of transport not only reduces carbon footprints but can also align with broader sustainability goals and initiatives.
- Awareness of travel choices and their environmental consequences can empower individuals to make more eco-friendly decisions for their journeys.

Understanding CO2 Emissions
To truly comprehend the impact of your travel choices on the environment, it is imperative to understand CO2 emissions. This greenhouse gas is primarily produced through the combustion of fossil fuels, such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. According to a report on Climate change: Should you fly, drive or take the train?, transportation significantly contributes to global CO2 emissions, making it a key area for anyone concerned about climate change and sustainability.
Definition of CO2 Emissions
For the purpose of this discussion, CO2 emissions refer to the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere as a result of various human activities, particularly in the transportation sector. These emissions accumulate in the atmosphere and contribute to the greenhouse effect, thus leading to global warming. The measurement of CO2 in travel is vital as it quantifies your carbon footprint, which is the total amount of greenhouse gases you are responsible for, expressed in CO2 equivalence.
Sources of CO2 Emissions in Transportation
Behind every mode of transportation, there are various sources responsible for generating CO2 emissions. Air travel is known for its high emissions per passenger mile, mainly due to the fossil fuels consumed during flights. On the other hand, cars emit CO2 largely depending on factors such as fuel efficiency, the type of fuel used, and the distance traveled. Trains and ferries generally have lower emissions per passenger but can still contribute significantly to the overall carbon footprint if not powered by renewable energy.
At the same time, it is worth noting that advancements in technology and shifts towards greener energy sources can help mitigate these emissions. Electric vehicles, hybrid models, as well as innovations in the aviation sector aiming to reduce fuel consumption, play a vital role in transitioning you towards more sustainable travel options.
Importance of Measuring CO2 Emissions
Before making any travel decisions, considering the importance of measuring CO2 emissions can guide you towards more sustainable options. Understanding the environmental impact of your choices empowers you to make informed decisions that align with your values. Furthermore, measuring CO2 emissions can help policymakers and businesses understand the overall impact of transportation on climate change, facilitating the development of more sustainable transportation systems.
Definition: By quantifying CO2 emissions, you not only track your individual contributions to climate change but also participate in broader environmental efforts. This awareness can motivate changes in behavior, from opting for public transport over driving to choosing destinations accessible by train or ferry, ultimately leading to a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Air Travel
Overview of Air Travel
Any discussion about efficient modes of transportation often includes air travel due to its speed and global reach. With the capability to connect distant locations in a matter of hours, air travel has become a staple for both leisure and business purposes. However, this convenience comes at a cost, particularly when it comes to environmental impact, making it important for you as a traveler to consider the implications of your choices.
CO2 Emissions per Passenger Mile
By understanding the CO2 emissions associated with air travel, you can make informed decisions about how you choose to travel. On average, flying an airplane generates around 0.2 to 0.4 kg of CO2 for each passenger mile traveled, which can add up significantly over long-distance flights. While flying may seem like the quickest option, this environmental cost presents a stark contrast to land or sea travel alternatives.
Around the world, the impact of air travel on climate change becomes more apparent—especially as passenger numbers rise. The aviation sector is expected to contribute up to 3% of global emissions, a figure that presents substantial challenges to international efforts for reducing greenhouse gases.
Travel by air has some of the highest carbon footprints of any form of transport. While airlines are increasingly working to develop more fuel-efficient planes, the immediate effects of air travel emissions continue to warrant attention and consideration as a traveler.
Factors Affecting Emissions in Aviation
With various factors influencing the emissions in aviation, understanding these can help you choose flights more wisely. Factors such as the type of aircraft, distance flown, and operational efficiency all play a significant role in the environmental footprint of air travel.
- Aircraft type – Newer models typically produce less emissions.
- Flight distance – Short-haul flights are less efficient than long-haul ones.
- Load factor – Higher passenger numbers reduce emissions per person.
The more efficiently an airline operates, the less your travel contributes to global warming. Understanding these variables will enable you to make greener choices when planning your trips.
Mile for mile, understanding the factors that affect emissions in air travel can empower you to reduce your carbon footprint as a traveler. Briefer layovers can also make a difference in fuel consumption, so consider these aspects when booking your next flight.
Innovations in Reducing Emissions
Against the backdrop of increasing awareness about climate change, the aviation industry is actively seeking ways to innovate and reduce its carbon footprint. From more efficient engines to sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs), these technical advancements promise to change the landscape of air travel for the better.
And as these innovations develop, they not only aim to minimize the negative impacts of aviation but can also provide exciting opportunities for travelers like you to make more sustainable choices. Investing in airlines that prioritize advancements in green technology can be a rewarding step toward lowering your personal environmental impact while still enjoying the benefits of air travel.

Rail Travel
Once again, you find yourself weighed with choices when it comes to sustainable travel options. Rail travel presents a compelling case as one of the more environmentally friendly means of transportation. Its efficiency and relatively low carbon footprint can make it an attractive alternative to planes and ferries when considering your journey.
Overview of Train Travel
One of the primary benefits of train travel is its capacity to transport large numbers of passengers simultaneously. This means that each individual on board benefits from a reduced per-person impact on the environment. Rail networks often connect urban and rural areas alike, providing a flexible option for various travel requirements while maintaining a smaller ecological footprint than other modes of transport.
CO2 Emissions per Passenger Mile
On the subject of emissions, studies show that train travel typically results in significantly lower CO2 emissions per passenger mile compared to road or air transport. For instance, taking a train can result in as much as 75% less CO2 emitted per mile than traveling by air, and up to 50% less compared to driving alone in a car. This stark difference highlights the effectiveness of rail travel as a sustainable alternative.
Due to the combination of electric trains, which may even be powered by renewable energy sources, along with the high capacity for passengers, the CO2 emissions associated with rail travel can be remarkably low. When planning your trips, considering rail as an option could significantly reduce your travel-related carbon footprint.
Factors Affecting Emissions in Railway Transportation
Along with the inherent advantages of rail, various factors can influence the emissions generated during your journey. These factors include the type of fuel used for locomotives, the age and efficiency of the trains in service, and the overall occupancy levels. Notably, higher occupancy rates lead to decreased emission per passenger, making it vital for you to choose and promote train options that prioritize full capacity.
- Fuel type
- Train efficiency
- Occupancy levels
Transportation advancements also play a key role in shaping your experience when traveling by train. Electric trains and those equipped with the latest technology can drastically reduce emissions. Assume that when you opt for environmentally-friendly and efficient train choices, you actively contribute to minimizing the overall impact on our planet.
Advances in Sustainable Rail Technologies
Travel in the rail industry is evolving at a rapid pace, especially with advances in sustainable rail technologies. Innovations such as hydrogen fuel cells and battery-powered trains are being developed to further reduce the reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, improvements in rail infrastructure and vehicle design contribute to decreased energy consumption, making it easier for you to choose a sustainable option.
A focus on developing greener rail systems not only benefits the environment but also enhances passenger experience through quieter, smoother journeys. Such advancements not only demonstrate a commitment to sustainability but also present you with exciting, efficient methods of transportation that align with changing societal values around the importance of reducing carbon emissions.

Ferry Travel
After evaluating different modes of transportation, let’s examine into ferry travel. Ferries have long been a staple for crossing bodies of water, connecting islands and coastal cities while providing a unique travel experience. For many travelers, ferries represent not just a means of movement, but also an opportunity to enjoy scenic views and commence on a leisurely journey. Given their presence in various regions around the world, ferries can vary significantly in design, purpose, and environmental impact.
Overview of Ferry Transportation
For individuals in many coastal communities, ferries play a vital role in daily life. They provide vital links, transporting both passengers and vehicles across waterways that might otherwise require lengthy detours. Additionally, ferries can accommodate larger groups, making them a popular choice for family vacations, group outings, and freight transport. Whether you’re considering a short trip or a longer voyage, understanding the role of ferries in your travel plans is beneficial.
CO2 Emissions per Passenger Mile
The environmental footprint of ferry travel is often analyzed through the lens of CO2 emissions per passenger mile. This metric helps you gauge the sustainability of different travel options and make informed decisions based on your environmental impact preferences. Generally, ferry travel can yield relatively low emissions compared to other modes of transport, especially when fully loaded. However, exact figures can vary widely depending on factors such as the vessel’s size, technology, and fuel source.
Due to the substantial capacity of ferries, they often boast a favorable CO2 emissions rate when transporting multiple passengers. A fully loaded ferry can have emissions comparable to those of a bus, which means that traveling on a ferry can be a more environmentally friendly option compared to driving your car or flying. This aspect is particularly relevant in a world increasingly focused on reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Factors Affecting Emissions in Ferry Services
An array of elements influences the emissions associated with ferry services. Key factors include the size and design of the vessel, the type of fuel utilized, and the efficiency of the operational practices in place. Understanding these factors can help you choose a ferry service that aligns with your environmental values. Some of the most notable contributors include:
- Vessel Size: Larger ferries may spread their emissions over more passengers, lessening the impact per person.
- Fuel Type: The choice between conventional fuels and alternative energies can drastically alter the emissions profile.
- Operational Practices: Efficient routing and voyage planning can minimize fuel consumption and emissions during trips.
Any traveler should consider these factors when evaluating their options for ferry travel.
Understanding these dynamics can further enhance your knowledge about ferry services. With advancements in technology, many ferry operators are prioritizing sustainability and aiming for lower emissions. You might find that some ferries are designed with innovative features that reduce fuel consumption and promote eco-friendly technologies. Consider the impact of the following:
- Hybrid Engines: Utilizing a combination of traditional fuel and electric power can reduce emissions compared to conventional engines.
- Aerodynamic Designs: Improved vessel shapes can minimize drag, leading to better fuel efficiency.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Some modern ferries are harnessing wind or solar power, promoting sustainability.
Any advancements in ferry technology can positively influence your travel experience by providing more eco-friendly options.
Innovations in Eco-friendly Ferries
Emissions reduction in the ferry industry is increasingly supported by innovative solutions aimed at decreasing the environmental impact of marine travel. You may find that many ferry operators are adopting eco-friendly technologies, including hybrid engines, renewable energy sources, and advanced hull designs to improve fuel efficiency. These innovations promote a greener approach to maritime travel, offering more sustainable alternatives for the environmentally conscious traveler.
Ecofriendly initiatives in ferry services not only promise lower emissions but also demonstrate the industry’s commitment to sustainable practices. Research and development efforts are ongoing, focusing on environmentally safe materials and construction techniques that align with regulations and consumer preferences. Additionally, as consumer demand for sustainable travel options increases, you’ll likely witness an even greater commitment from ferry companies to reduce their carbon footprint in the future.
Comparative Analysis of CO2 Emissions
All modes of transportation have varying levels of CO2 emissions associated with them. Understanding these differences can help you make informed travel choices that align with your environmental values. Below is a comparative analysis showing average emissions per passenger kilometer for planes, trains, and ferries.
| Travel Mode | Average CO2 Emissions (g/km/pax) |
|---|---|
| Plane | 285 |
| Train | 14 |
| Ferry | 75 |
Direct Comparison of Travel Modes
Beside the emissions discussed above, it’s important to consider that planes contribute significantly higher levels of greenhouse gases when compared to other modes of transport. Air travel is typically viewed as one of the least environmentally friendly options, especially for short distances. In contrast, trains are often hailed as a more sustainable choice, emitting far less CO2 per passenger mile. Ferries sit somewhat in the middle, providing a balance between effective transport and moderate emissions.
When planning your journey, you should weigh these figures against other factors like convenience and travel time. While flying may be quicker, the large carbon footprint may make you reconsider, especially if alternatives are accessible. Trains offer a low-emission travel option and quite often are more scenic, potentially delivering a more enriching travel experience.
Regional Variations in Emissions
Travel patterns and the energy sources used for transportation can greatly influence the regional variations in emissions. In some areas, trains might rely on electricity generated from fossil fuels, leading to increased emissions compared to regions where the electricity comes from renewable sources. Ferries operating in areas with stricter emissions regulations might also display different data in terms of their environmental impact, depending on their fuel efficiency and the technology in use.
Notably, urban regions with well-established rail networks often have lower emissions per passenger compared to rural areas where transport options might rely heavily on single-passenger vehicles or older, less efficient modes of transport. Understanding these regional dynamics can empower you to make travel choices that are more environmentally mindful.
Analysis of travel emissions also reveals the impact of infrastructure and policies in different regions. Locations that promote public transportation and renewable energy sources show significantly reduced overall emissions, showcasing the potential for change when communities prioritize sustainability.
Life Cycle Assessment of Travel Options
After evaluating direct emissions, a comprehensive approach to understanding travel’s environmental impact involves conducting a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). This assessment takes into account not just the emissions generated during travel but also those associated with the vehicle manufacturing, maintenance, and eventual disposal. It creates a more complete picture of your carbon footprint for any given travel option.
By incorporating LCA into your travel planning, you can better appreciate the broader implications of your transport choices. For instance, while trains may have low operational emissions, the carbon costs associated with rail infrastructure and rolling stock production can alter the LCA findings. Thus, understanding the full lifecycle will further inform your decisions.
The benefits of conducting an LCA extend beyond individual travel choices. Policymakers can utilize such assessments to develop strategies that encourage cleaner technology and energy-efficient practices in the transportation sector, significantly impacting the mitigation of climate change.
Policy and Environmental Impact
Unlike many personal assumptions about travel, the method you choose greatly impacts the environment. Air travel is notorious for high CO2 emissions: Train & ferry versus plane, making it one of the most significant contributors to global greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, trains and ferries generally emit far less CO2 per passenger, highlighting the importance of considering greener alternatives when planning your next trip.
Global Initiatives to Reduce Transportation Emissions
For your travel choices to have a meaningful impact, you should be aware of global initiatives aimed at reducing transportation emissions. Various countries and international organizations have committed to cutting down carbon footprints by promoting sustainable travel methods, enhancing public transportation, and investing in cleaner energy sources. Efforts like the European Union’s Green Deal and various United Nations initiatives encourage a shift towards low-carbon options that significantly lessen the environmental toll of travel.
Role of Government in Promoting Sustainable Travel
Between the frameworks established by policymakers and the responsibility placed on individuals, governments play a fundamental role in promoting sustainable travel. By setting regulations and incentives for greener transportation, they can shift public behavior towards more environmentally-friendly options. Such measures might include subsidies for electric public transport, funding for cycling infrastructure, or mandating emissions reductions for airlines.
At the local level, governments can engage with communities to develop sustainable travel programs. This helps you see the benefits of using less polluting modes of transport, such as public transport systems, bicycles, and electric vehicles. When governments take the lead, they send a strong message about the importance of shifting our travel habits to align with environmentally sustainable goals.
Public Awareness and Individual Responsibility
On a personal level, your awareness and choices have a significant effect on the environment. Understanding the impact of your travel habits can empower you to make more informed decisions. By opting for lower-emission modes of transport, you actively contribute to reducing global CO2 emissions. Engaging in discussions about environmental issues and supporting policies for sustainable travel can further amplify your positive impact.
Initiatives to raise public consciousness about travel emissions remind you that your everyday choices matter. Whether it’s participating in local sustainability programs or opting for eco-friendly transport options, you can drive change in your communities. Individual responsibility plays a vital role in creating a collective force for environmental protection, illustrating how each travel decision contributes to a larger goal of reducing our carbon footprints.
Conclusion
To wrap up, understanding the impact of your travel choices on CO2 emissions is imperative for fostering a more sustainable future. When you consider airplane travel, train journeys, and ferry rides, the significant differences in carbon footprints become evident. Air travel tends to generate the highest emissions per mile per passenger, while trains often emerge as the most eco-friendly option, particularly if powered by renewable energy. Ferries fall somewhere in between, with their environmental impact varying widely based on the type of vessel and operational efficiency.
As you make decisions about your travel plans, be conscious of how these choices affect not only your personal carbon footprint but also the environment at large. Opting for trains when feasible or considering ferries for shorter trips can significantly reduce your CO2 emissions in comparison to flying. By prioritizing greener travel options, you not only contribute to the fight against climate change but also encourage a broader shift towards sustainable transportation practices within society.
FAQ
Q: What mode of transport generally has the lowest CO2 emissions per passenger mile?
A: Trains typically have the lowest CO2 emissions per passenger mile compared to planes and ferries. Rail travel generally emits less greenhouse gas due to their efficiency in fuel usage and the ability to transport a larger number of passengers at once.
Q: How do CO2 emissions from planes compare to those from ferries?
A: Planes usually emit more CO2 per passenger mile than ferries, especially for shorter distances. While ferries can also have significant emissions, particularly if they are large and use heavy fuel, planes tend to have higher emissions due to the high energy demand of aviation fuel and the altitude at which they operate.
Q: What factors influence the CO2 emissions of different transport modes?
A: Several factors influence CO2 emissions, including distance, type of fuel used, the efficiency of the vehicle, load factor (number of passengers or amount of cargo), and the specific route taken. For instance, direct flights or train routes can result in lower emissions compared to connections requiring layovers or transfers.
Q: Are there any emissions offsets available for air travel?
A: Yes, many airlines offer carbon offset programs that allow passengers to contribute to projects aimed at reducing emissions, such as reforestation or renewable energy initiatives. However, it is important for travelers to research and choose credible offset programs to ensure their investments truly contribute to emission reductions.
Q: What is the impact of choosing a high-speed train over a low-speed train in terms of emissions?
A: Generally, high-speed trains can emit more CO2 than standard trains due to their greater energy consumption during acceleration and higher speeds. However, when considering the overall capacity and the number of passengers transported, high-speed trains can still maintain lower emissions per passenger mile compared to planes.
Q: Are there any seasonal variations in the CO2 emissions for these transport modes?
A: Yes, seasonal variations can affect CO2 emissions for transport modes. For example, airlines may operate more flights during peak seasons, leading to increased emissions. Similarly, ferry services might see higher traffic in summer months. Additionally, weather conditions can influence ferry and rail operations, potentially affecting their efficiency.
Q: How does public transport, like buses, compare to planes, trains, and ferries regarding CO2 emissions?
A: Public transport such as buses typically has lower CO2 emissions per passenger mile compared to planes and ferries, especially when fully loaded. Buses can be one of the most environmentally friendly options for travel, depending on the fuel used and the efficiency of the vehicle. Trains usually still outperform buses in terms of capacity and emissions, but buses are often more accessible for short distances.

Our contributing author is a passionate advocate for eco-friendly living and sustainability. With a background in eco-life, they are dedicated to inspiring and empowering individuals to adopt environmentally conscious lifestyles. Through insightful articles, they share practical tips, innovative solutions, and thought-provoking perspectives to promote a greener, more sustainable world. Join them on the journey towards eco-smart living and discover how small choices can make a big impact. 🌱